Earth Battery Voltage: Everything You Need to Know
Ever wonder if the ground beneath your feet could be a power source? It sounds almost too futuristic, but the concept of Earth battery voltage has been around for quite some time. It harnesses the Earth’s natural electric potential to generate energy. Unlike traditional batteries that rely on chemicals to store power, Earth batteries tap into the Earth’s natural conductivity, using a simple setup of metal electrodes and moist soil.
But why should you care about Earth battery voltage? As the world leans toward more sustainable and renewable energy solutions, this old-school technology has started to gain renewed attention. It offers a potential alternative power source for remote locations and low-energy devices and opens up intriguing possibilities for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint. Whether you’re a curious eco-enthusiast or simply exploring the world of off-grid energy solutions, Earth battery voltage is an innovative concept that could become a game changer in the future of energy generation.
Understanding Earth Battery Voltage and Its Relevance
So, what makes Earth battery voltage such a compelling subject? To start, the concept is as intriguing as it is practical. The Earth can act as a low-maintenance power source with its naturally occurring electric currents. An Earth battery can generate small amounts of electricity using a pair of dissimilar metals embedded in moist soil. This may sound like something out of a science experiment, but it’s rooted in real-world applications that could revolutionize energy sustainability.
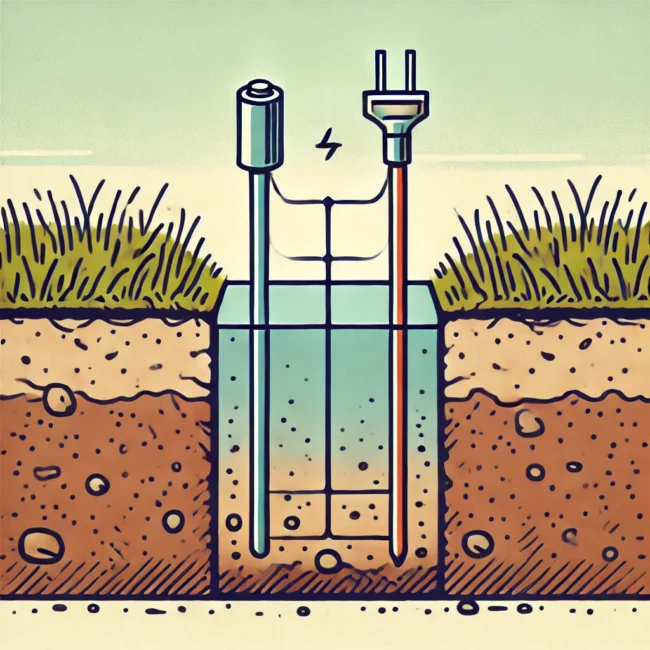
The allure of Earth battery voltage lies in its potential for decentralized, eco-friendly power generation. Imagine having a power source that doesn’t rely on the grid, solar panels, or wind turbines. Instead, you’re tapping into the very ground beneath your feet. While it may not power your home, Earth batteries can serve more minor needs—like powering sensors, low-energy devices, or remote off-grid equipment. This technology is innovative and timely in a world increasingly focused on reducing carbon emissions.
Here’s why the topic of Earth Batteries is crucial:
- Sustainability: Earth batteries rely on the planet’s natural conductivity, eliminating the need for chemical reactions or harmful materials used in conventional batteries.
- Off-grid capabilities: Earth battery technology provides a simple and renewable alternative to power low-energy devices for remote areas or places lacking energy infrastructure.
- Cost-effective: Since the primary “fuel” for an Earth battery is the soil itself, maintenance and operation costs are minimal. Once set up, it can generate power with little to no input.
- Eco-conscious solution: Unlike traditional energy sources that rely on finite resources, Earth battery voltage taps into a renewable and nearly limitless energy source, aligning with sustainability and environmental preservation goals.
How Earth Batteries Work: The Science Behind the Power
Earth battery voltage may sound like magic, but its science is fascinating and straightforward. At its core, an Earth battery utilizes the natural electrical potential difference between two dissimilar metals buried in moist soil. The soil acts as an electrolyte, allowing ions to move between the metals, thus generating electricity. This process is reminiscent of traditional batteries operating without relying on corrosive chemicals. Instead, Earth batteries tap into the naturally occurring electric fields in the ground to create power.
The basic setup involves inserting two electrodes—usually metals with differing electrochemical properties—into the Earth. A typical combination includes copper and zinc rods, where copper acts as the positive electrode (cathode) and zinc as the negative electrode (anode). The soil provides the conductive medium, and its moisture allows ions to flow between the two metals, creating a voltage. The greater the distance between the electrodes and the more conductive the soil, the higher the voltage output.
To further understand how this technology stacks up against other renewable energy solutions, here’s a simple comparison:
| Parameter | Earth Battery | Solar Power | Wind Power |
| Energy Source | Natural Earth conductivity | Sunlight | Wind movement |
| Setup Cost | Low (basic materials like copper and zinc) | High (panels, inverters, batteries) | High (turbines, installation costs) |
| Maintenance | Minimal (once installed, requires little upkeep) | Moderate (panels need occasional cleaning) | High (moving parts require regular service) |
| Power Output | Low (suitable for small devices, sensors) | Moderate to high (can power homes or industries) | Moderate to high (depending on wind speed) |
| Environmental Impact | Very low (no emissions or harmful byproducts) | Low (but manufacturing panels have some impact) | Low (turbine production has a moderate impact) |
| Scalability | Limited (more suited for low-energy needs) | High (can be scaled for homes or businesses) | High (suitable for large-scale projects) |
Advantages of Earth Batteries:
- Low Impact, High Return: The components needed for an Earth battery are inexpensive and easy to source, making it an accessible energy solution for anyone.
- No Emission: Unlike fossil fuels or even some renewable energy sources that require extensive manufacturing, Earth batteries are almost entirely carbon emissions-free.
- Suitable for Remote Areas: Earth batteries require little infrastructure, making them ideal for powering devices in off-grid locations.
Applications of Earth Batteries: Where Can This Technology Be Used?
While Earth battery voltage may still need to be the primary power source for homes or industries, it holds significant potential in specific applications. This technology thrives in low-energy environments where small but reliable power outputs are necessary. From remote locations to educational projects, Earth batteries serve a unique niche that can fill gaps in the renewable energy landscape.
- Remote Sensors and Monitoring Equipment Imagine a forest monitoring system that tracks wildlife or environmental changes. These devices typically require very little energy, making them ideal candidates for Earth batteries. Earth batteries are an excellent fit for long-term, low-maintenance energy solutions because they can be installed virtually anywhere without relying on solar exposure or consistent wind.
- Off-Grid and Survivalist Solutions Self-sufficiency is critical for those living off the grid. Earth batteries provide an alternative energy source for small-scale applications, such as powering LED lights, radios, or small electronics. While they won’t replace more robust off-grid systems like solar panels, Earth batteries can serve as a backup power source or supplement existing renewable energy solutions.
- Educational and Experimental Projects In schools, Earth batteries offer a fantastic hands-on learning tool for teaching the basics of electricity, renewable energy, and sustainability. Students can quickly build and observe the function of an Earth battery with simple materials, giving them insight into how natural energy can be harnessed. This concept bridges the gap between science education and environmental awareness, offering a unique and memorable classroom experience.
- Emergency Power In survival situations or during natural disasters when the primary power grid is down, Earth batteries can provide a small but vital power source. While they won’t charge your phone or run appliances, they could power emergency devices like small radios or flashlights. The simplicity of the setup makes it an attractive option when resources are scarce and conventional power sources are inaccessible.
Powering the Future with Earth Batteries:
- Agricultural Monitoring: Soil moisture sensors or weather stations in remote farming areas can run on Earth batteries, ensuring continuous data collection without human intervention.
- Military Applications: Earth batteries can provide an undetectable, sustainable power source for small devices like communication tools or surveillance systems in challenging terrains or remote outposts.
- Eco-Friendly Landscaping: Earth batteries could power low-energy lighting systems or decorative features in urban gardens or sustainable landscaping without any environmental impact.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Build Your Earth Battery
Building your own Earth battery might sound like something from a science fiction novel, but it’s a simple, DIY-friendly project requiring minimal materials. If you’re curious about generating power from the ground beneath you, here’s a step-by-step process to get your Earth battery up and running.
Step 1. Gather Your Materials: Before you start, make sure you have the suitable materials on hand. Earth batteries require only a few essential components, most of which are easily accessible:
- Copper rod (cathode)
- Zinc rod (anode)
- Alligator clips or copper wiring
- Multimeter (to measure voltage)
- Moist soil or a small patch of ground
- Container (if you’re not using direct soil)
- Water (optional for extra moisture)
Step 2. Prepare the Soil: The key to an efficient Earth battery is moisture. Dry soil won’t conduct electricity well, so lightly water the area where you plan to insert the electrodes if necessary. If you’re using a container, fill it with soil and moisten it until it feels damp.
Step 3. Insert the Electrodes: Now, place your copper and zinc rods in the soil. Position them a few inches apart to allow the electric potential to form between the two metals. The copper rod will act as the cathode (positive terminal), while the zinc rod will serve as the anode (negative terminal). The distance between them plays a role in the voltage generated—the further apart, the higher the potential difference, although a few inches should suffice for a basic setup.
Step 4. Connect the Wires: Using alligator clips or copper wiring, connect the copper rod to the positive terminal of your multimeter and the zinc rod to the negative terminal.
Step 5. Measure the Voltage: Now comes the exciting part—measuring your Earth battery’s voltage. Please turn on your multimeter and set it to measure DC voltage. A small voltage reading should appear on the screen, typically 0.5 to 1.0 volts. The reading may fluctuate slightly depending on the soil’s moisture content and the distance between the electrodes.
Step 6. Troubleshoot and Optimize: If you’re not seeing a voltage reading or the reading is too low, try these troubleshooting tips:
- Increase the moisture by adding a little more water to the soil.
- Reposition the electrodes to increase the distance between them.
- Different metals can also be used for the electrodes (aluminum can also work).
- Test in different soil types to see which yields the highest voltage.
Step 7. Scale It Up: Once you’ve successfully generated power from your Earth battery, you can experiment with scaling it up. You can create a series of Earth batteries by connecting multiple cells in series (copper to zinc, and so on) to increase the total voltage output. This is a great way to power small devices or explore the potential for off-grid energy solutions.
Step 8. Put It to Use: While a single Earth battery won’t power your home, it can be a learning tool or even provide enough energy to run small devices like LED lights, clocks, or low-energy sensors. The possibilities are endless, and you can integrate Earth battery technology into various low-power projects with some creativity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Earth Battery Voltage
As Earth battery technology gains traction among eco-enthusiasts and DIYers, many question how it works and its potential uses. Here’s a breakdown of the most frequently asked questions to help clarify the concept and its applications. These answers are designed to be clear and unique and avoid repetitive wording from other resources.
What exactly is an Earth battery?
An Earth battery is a simple device that generates electricity by harnessing the Earth’s natural conductivity. It uses two dissimilar metals, copper and zinc, inserted into moist soil. The Earth acts as an electrolyte, allowing ions to move between the metals and generating a small voltage. It’s a natural version of a traditional battery without the need for manufactured chemicals or materials.
How much power can an Earth battery generate?
Earth batteries typically produce low voltage, usually in the range of 0.5 to 1.0 volts per cell. The output depends on several factors, including the distance between the electrodes, the conductivity of the soil, and the moisture content. While it’s not enough to power large appliances, multiple cells can be connected to generate higher voltage for low-energy devices like LEDs, sensors, or small electronic gadgets.
What kind of soil works best for an Earth battery?
Moist, conductive soil works best for Earth batteries. Soil rich in minerals and with adequate moisture will allow ions to flow freely between the electrodes, improving the voltage output. Clay-rich soils or those near water sources tend to perform better than dry, sandy soils. However, you can always add water to increase the moisture content and enhance conductivity.
Can an Earth battery replace traditional power sources?
At this stage, Earth batteries are not designed to replace conventional power sources like solar or wind energy for large-scale electricity needs. Their low output suits small-scale applications, such as powering sensors, environmental monitoring systems, or small lights. Earth batteries are best seen as a supplemental or backup power option rather than a full-on replacement for the grid.
How long do Earth batteries last?
The lifespan of an Earth battery depends on the materials used and the soil conditions. Due to natural corrosion, copper and zinc electrodes tend to degrade slowly over time. Still, with proper care, an Earth battery can function for several months or even years before needing to be replaced. Keeping the soil moist will also extend its life and maintain its power output.
Are Earth batteries environmentally friendly?
They use natural resources—the Earth and metals like copper and zinc—to generate power. Moreover, they don’t produce emissions or require energy-intensive manufacturing processes like traditional batteries.
Can you increase the voltage of an Earth battery?
You can boost the voltage by connecting multiple Earth battery cells in series. This means linking one cell’s copper electrode to the next’s zinc electrode. By doing this, the voltage of each cell adds up, allowing for a higher total voltage output. This method can generate enough power to run slightly larger devices or multiple small gadgets.
What are some real-world uses for Earth batteries?
Earth batteries are handy in areas where traditional energy infrastructure is lacking. They can power small devices such as garden lights, environmental sensors, and other low-energy electronics in remote or off-grid locations. They’re also popular in educational settings, providing a hands-on way to teach electricity and renewable energy concepts. Moreover, they offer an excellent solution for hobbyists and experimenters interested in alternative energy sources.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Final Thoughts on Earth Battery Voltage
Earth batteries may not be the most well-known energy solution, but their simplicity, sustainability, and affordability make them a fascinating alternative for small-scale power generation. By harnessing the natural electric potential of the Earth using two dissimilar metals and moist soil as an electrolyte, Earth batteries offer a unique way to generate voltage without relying on conventional or harmful energy sources.
Key Takeaways:
- Earth batteries create voltage between two dissimilar metals (such as copper and zinc) buried in conductive, moist soil.
- These batteries produce low voltage—typically between 0.5 and 1.0 volts—making them suitable for powering small devices, sensors, or environmental monitors.
- While they aren’t a replacement for traditional renewable energy systems like solar or wind, Earth batteries are highly eco-friendly and require minimal maintenance.
- Earth batteries are versatile, finding applications in off-grid living, educational projects, remote sensors, and even emergencies where small, reliable power sources are needed.
In summary, Earth batteries represent an underappreciated piece of renewable energy technology. They provide an accessible, low-cost solution for low-power needs while contributing to sustainability efforts. Although not designed to power homes or large-scale systems, their role in the renewable energy landscape, especially in niche applications, is undeniable. With suitable materials and setup, anyone can explore the power of the Earth beneath their feet, making this a genuinely intriguing energy experiment.
Leave a Reply